Our goal is to boost our research output for 2026 by √2 over our previous year. We measure our research output by SNIP points, which are described in our Journals page. Help us reach our target of 80 points for this year.
Drafts

Dirichlet meets Kauffman
Long the province of statistical physics, the structure of the Kauffman model of genetic computation is uncovered via Dirichlet convolutions.

Number theory
Recursive divisor properties
The recursive divisor function is found to have a simple generating function, which leads to a number of new Dirichlet convolutions.
Singularities of discriminants
Investigating to what extent Whitney's theorem holds true for more general universal polynomials such as A-discriminants by Gelfand, Kapranov and Zelevinsky.
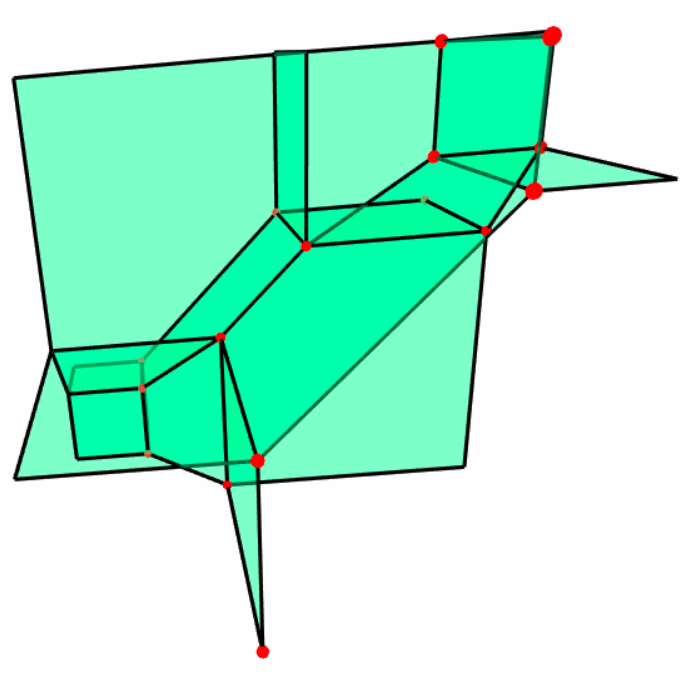
Algebraic geometry
Topology of tropical polynomials
Tropical geometric objects share many characteristics with classical algebraic geometry objects. We study this correspondence for the topology of polynomials.
MSSM vacuum structure
On the vacuum structure of the minimal supersymmetric standard model, which considers only particle states and interactions consistent with reality.
Arxiv

Synthetic biology
Cell soup in screens
Bursting cells can introduce noise in transcription factor screens, but modelling this process allows us to discern true counts from false.

Theory of innovation
Recursive structure of innovation
A theoretical model of recursive innovation suggests that new technologies are recursively built up from new combinations of existing ones.

Statistical physics
Deep learning simplicity
We give a theory for the output of deep-layered machines and show that, as the network depth increases, it is biased towards simple outputs.

Evolvability
I want to be forever young
The mortality equation governs the dynamics of an evolving population with a given maximum age, offering a theory for programmed ageing.
Algebraic geometry
Slight degenerations
The tools used to study polynomial equations with indeterminate coefficients are extended to some important cases with interrelated ones.
Algebraic geometry
Schön complete intersections
A uniform approach to a class of varieties is described that includes important types of objects from geometry, optimisation and physics.
Number theory
Ample and pristine numbers
Parallels between the perfect and abundant numbers and their recursive analogs point to deeper structure in the recursive divisor function.
Algebraic geometry
Symmetric spatial curves
We study the geometry of generic spatial curves with a symmetry in order to understand the Galois group of a family of sparse polynomials.
Integrable Systems
Exact hard-rod dynamics
A canonical quantum fluid model is solved exactly, revealing universal correlation patterns governed by Gaussian random-matrix ensembles.
Number theory
Recursive divisor properties
The recursive divisor function has a simple Dirichlet series that relates it to the divisor function and other standard arithmetic functions.
Number theory
Counting recursive divisors
Three new closed-form expressions give the number of recursive divisors and ordered factorisations, which were until now hard to compute.
Evolvability
Flowers of immortality
The eigenvalues of the mortality equation fall into two classes—the flower and the stem—but only the stem eigenvalues control the dynamics.
Condensed matter theory
Counting free fermions
We link the statistical properties of one-dimensional systems of free fermions initialised in states of either half- or alternating-occupancy.
Computational linguistics
Cross-lingual knowledge
Models trained on a Russian topical dataset, of knowledge-grounded human-human conversation, are capable of real-world tasks across languages.
Machine learning
Boosting AI reasoning
By increasing the effective depth of neural networks, we improve their sequential reasoning abilities in tasks involving cellular automata.
Machine learning
Limits of attention
We demonstrate that transformer attention can only discriminate well at shorter context lengths, losing clarity as input length increases.
Representation theory
Group representations
A general approach to proving the irreducibility of representations of infinite-dimensional groups within the frame of Ismagilov's conjecture.
Submitted home
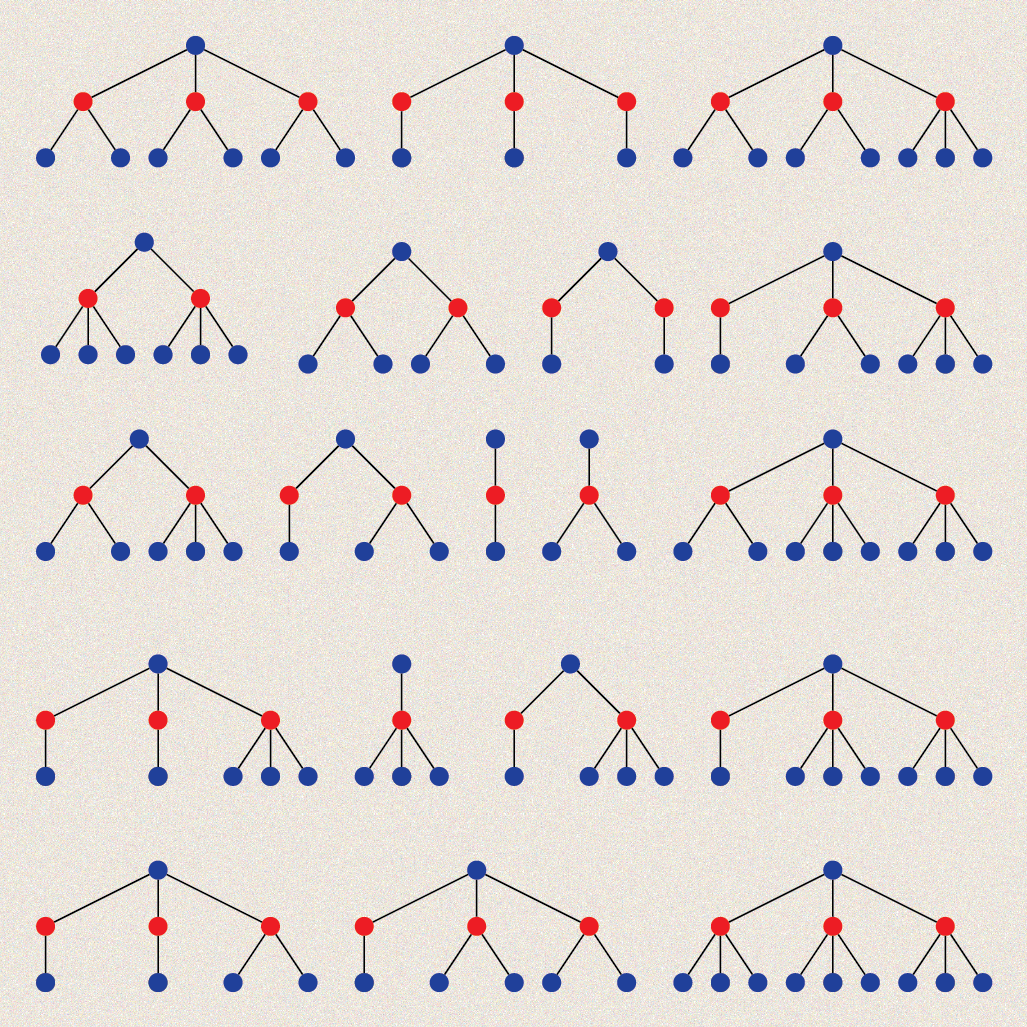
Combinatorics
In life, there are few rules
The bipartite nature of regulatory networks means gene-gene logics are composed, which severely restricts which ones can show up in life.

Combinatorics
Structure of genetic computation
The structural and functional building blocks of gene regulatory networks correspond, which tell us how genetic computation is organised.

Combinatorics
Biological logics are restricted
The fraction of logics that are biologically permitted can be bounded and shown to be tiny, which makes inferring them from experiments easier.
Submitted away

High energy physics
Topological dark matter
Sterile neutrinos are replaced by topological order as dark matter candidates to counterbalance the Standard Model’s gravitational anomalies.

Combinatorics
Representation for sum-product
A new way to estimate indices via representation theory reveals links to the sum-product phenomena and Zaremba’s conjecture in number theory.

Number theory
Bounding Zaremba’s conjecture
Using methods related to the Bourgain–Gamburd machine refines the previous bound on Zaremba’s conjecture in the theory of continued fractions.
Algebraic geometry
Permuting the roots
The Galois group of a typical rational function is described and similar problems solved using the topology of braids and tropical geometry.
High energy physics
A new leptogenesis
We propose that dark matter consists of topological order, so gapped anyon excitations decay to generate the Standard Model's lepton asymmetry.
AI-assisted maths
Learning integrability
We introduce an AI-based framework for finding solutions to the Yang-Baxter equation and discover hundreds of new integrable Hamiltonians.
Quantum physics
Towards optimal control
Time-optimal control of large quantum systems is computed efficiently by applying boundary conditions to a brachistochrone–Lax framework.
Quantum physics
Regularising CRT
Charge conjugation C, space reflection R, and time-reversal T operators are regularised in a quantum many-body Hilbert space on a discrete lattice.
Algebraic geometry
Sparse singularities
Geometric properties, including delta invariants, are computed for singular points defined by polynomials with indeterminate coefficients.
High energy physics
Fermionic dark matter
Gravitational anomalies causing baryon and lepton number violation in the Standard Model are resolved using new fermionic topological orders.
Algebraic geometry
Linearising actions
We give a solution of the linearisation problem in the Cremona group of rank two over an algebraically closed field of characteristic zero.
High energy physics
An 8-fold way for CRT
Varying the spacetime dimensions fermions occupy shows charge-conjugation C, space-reflection R and time-reversal T symmetries are 8-fold periodic.
High energy physics
Topological responses
Fractional conductivity between the nuclear and electromagnetic higher symmetries reveals four global Lie gauge groups of the Standard Model.
Algebraic geometry
Analysing the vacuum
Birational methods in algebraic geometry are used to explicitly describe the vacuum structure of the Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model.
Published

Number theory
Higher energies
Generalising the recent Kelley–Meka result on sets avoiding arithmetic progressions of length three leads to developments in the theory of the higher energies.
AI-assisted maths
AI for error correction
Machine learning finds “champion” codes by predicting and optimising their minimum Hamming distance, a measure of a code’s robustness.